What is the Extraction Process from Crude Oil Reserves?
The Extraction Process from Crude Oil Reserves is known as petroleum refining or oil refining. Several stages are required to separate and purify the various components of crude oil, including gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel.
Crude Oil Introduction
Crude oil is one of the most essential fossil fuels in the world; it is also known as “black gold.” Coal is abundantly available on the planet and is less expensive than oil. Petroleum is not available in all locations. This article will discuss crude oil, its exploitation, and the largest oil-producing nations.
What exactly is Crude Oil?
Crude oil consists of organic compounds and hydrocarbons. It formed thousands of years ago when deceased organisms were subjected to intense pressure and heat deep within the earth. As the name implies, crude means unrefined; therefore, crude oil is not refined. The extraction of crude oil involves drilling processes. Crude oil is a form of fossil fuel that can be refined into various useful products, such as diesel, petrol, heating oil, kerosene, LPG, etc. Black treasure is an unofficial nickname for crude oil.
History of Crude Oil:
It is fascinating to learn how Crude oil In the 20th century, it became a significant economic factor. Although only a handful of nations control vast reservoirs. Historically, petroleum oil was utilized in numerous countries, including China, Iran, France, etc., but they have yet to reach a significant milestone.
- The petroleum oil industry began to flourish in the 18th century.
- The industrial revolution marked the actual use of Crude oil, at which point the world became aware of the true strength of Oil.
- In 1837, a commercial oil refinery was constructed in Baku. As its significance developed, countries such as Poland, Romania, Canada, the United States, etc., followed suit.
- A chemist established a modest business refining crude oil in 1848.
- The first oil refinery was established in 1856.
- In 1854, the first modern oil well was sunk.
- World conflicts fueled the oil demand. Oil prices increased.
- Pennsylvania’s prices increased dramatically from $0.49 per barrel to $6.59 per barrel, approximately 59 times. It produced fifty percent of the world’s hydrocarbons.
- In the late nineteenth century, the United States was one of the largest oil producers in the world.
- The Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) comprises key oil-exporting nations. It was established in 1960 to help provide fuel to countries in need.
- New technologies significantly diminished OPEC’s role and influence.
- Petroleum is one of the world’s most valuable commodities because it is a portable, dense energy source that powers most vehicles and serves as the foundation for various industrial compounds. Saudi Arabia, Russia, and the United States are currently the top three oil producers.
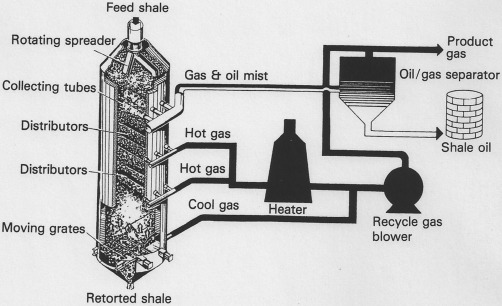
How Petroleum Products are Extracted from Crude Oil
The extraction of petroleum products from crude oil is complex and time-consuming; here, we detail the entire extraction procedure.
- After drilling, extraction, and recovery, first-use petroleum exploration occurs.
- Recovered crude oil cannot be used directly; it must be transformed or converted into consumable forms.
- The initial procedure for refining crude oil is to bring it to a boil.
- The bubbling liquid is separated into liquids and gases via distillation. Petrol, paraffin, diesel fuel, etc. are produced from these compounds.
- As gases ascend a column, they chill to the point where they condense (turn back into liquid). After purification and additional processing, the separated liquids and gases are used to produce various goods.
- Afterward, liquids can be transformed into other beneficial forms via various processes. The heavier a liquid is, the lower its demand.
- On a refinery’s tank farm, enormous tanks temporarily store outgoing finished goods. Automobiles transport final products from storage containers to their final destinations.
Refining crude oil into various products:
- Crude oil is a mixture of numerous components. But to use them, crude oil must be refined.
- Oil refineries are the sites of refinement.
- Through distillation, crude oil is first separated into various forms. In the distillation chamber, denser substances sink to the bottom, and lighter substances rise to the top.
- The second phase is conversion, in which denser solids are transformed into liquids or gases. This process is chemical in nature.
- In the final and third stages, work must be done because impurities remain. The process of obtaining products in their purest forms to use them is known as treating.
Major products after refining:
Petroleum products are by-products of petroleum oil refining. Depending on the crude oil refinery, different petroleum products may be manufactured. The preponderance of petroleum products, including various types of fuel oil, are used as energy carriers. When refined, fuels can be combined to create more valuable substances. For instance, gasoline, aviation fuel, and diesel oil can be connected to create more efficient forms. Refined products can be used to produce plastics and other valuable items.
Gasoline.
- After refining crude oil, the vast majority of gasoline is produced. It accounts for 46% of the total products obtained.
- Also known as gasoline, it is intensely combustible.
- It is a standard primary fuel in internal combustion engines.
- It is also employed in dry cleaning.
Diesel and additional fuels
- Diesel oil comprises 20% of the products obtained, while other fuels account for 6%.
- Diesel oil is explosive and is typically used in large vehicles.
- Diesel oil is preferred for use in tanks and vehicles because it is less explosive.
- In addition, diesel is used to power large electric generators.
Kerosene.
- 8% of the total is also known as paraffin oil, which is derived from petroleum.
- It is flammable and translucent.
- Primarily used for domestic purposes, such as lighting, cooking, and heating.
Wax Composed of Paraffin
- During petroleum oil refining, paraffin wax is also extracted as a solid.
- Paraffin wax is well-known in the candlemaking industry.
- Other frequent applications include lubricants, ointments, ink, and electrical insulation.
Asphalt.
- Asphalt comprises 3 percent of the total output.
- It has a liquid or semi-solid consistency.
- The principal application of asphalt is the construction of roads.
- Also used for waterproofing the ceilings of the rooftops.
Lubricants.
- Lubricants make up one percent of the total.
- Typically, lubricants are used to reduce friction between objects.
- Lubricants include motor lubricants and greases.
- Also used to prevent machine corrosion.
LPG.
- LPG is hugely explosive in its natural state.
- LPG is primarily used for thermal purposes in the home. Additionally, it is utilized in industries.
Other obtained products might be in less quantity may include:
- Petroleum Coke.
- Sulfur.
- Naphtha.
- Tar.
- Jet fuel.
Major Oil-producing Countries.
In 2021, total world oil production averaged 77,043,680 barrels per day, of which 71% came from the top 10 nations. The following is a list of countries by oil production for the calendar year 2021, compiled by the US EIAD:
- United States
- Russia
- Saudi Arabia (OPEC)
- Canada
- Iraq (OPEC)
- China
- Iran (OPEC)
- UAE (OPEC)
- Brazil
- Kuwait (OPEC)
- Norway
- Kazakhstan
- Mexico
- Nigeria (OPEC)
- Qatar
Since 2014, the top three producers have produced 11 million barrels per day. The monthly oil production in the United States surpassed 12 million barrels in 2019 and 18 million barrels per day in 2021. Oil is measured in barrels and metric tonnes, each containing 42 liters of oil.
Conclusion.
According to reports from the United States, the globe consumed 98.8 million barrels of oil per day in 2017. Consequently, the rise in the number of vehicles is primarily responsible for the rise in oil consumption in the twenty-first century. Oil production will result in various outcomes, such as increased exploration of oil reservoirs leading to higher oil prices. People are raising concerns about the long-term viability, expenditures, and production of oil and their impact on the future.
Weirdnewsera says that you might not find any other platform that gives you all the content about health, sports, business, technology, and entertainment.
FAQs
Certainly! The following are frequently asked questions (FAQs) regarding gasoline extraction from crude oil.
What is gasoline, and why is it derived from crude oil?
Petrol, also known as gasoline, is a liquid fuel primarily used as an automobile fuel. It is a valuable product derived from petroleum oil due to its high energy content and suitability for internal combustion engines, making it an indispensable component of the contemporary transportation industry.
How is gasoline derived from petroleum oil?
Petrol is extracted from crude oil through the petroleum refining or oil refining process. In fractional distillation, crude oil is heated in a distillation column to separate its components based on their distinct boiling points. The gasoline fraction, as well as other products such as diesel and aviation fuel, is gathered and further refined to meet the desired quality standards.
What precisely is fractional distillation?
A: Fractional distillation is a refining procedure that separates crude oil into fractions based on the components’ boiling points. As crude oil is heated in a distillation column, the various hydrocarbons in the crude oil evaporate at different temperatures and condense at different heights within the column, enabling the separation of various products.
What are the primary steps in the refining procedure for gasoline extraction?
- The most important stages in the refining process for gasoline extraction are:
- Utilizing fractional distillation to separate crude oil into its constituent fractions.
- Additional refining processes such as reforming, isomerization, alkylation, and hydrodesulfurization are utilized to improve the quality of gasoline.
- Blending to obtain the desired characteristics and specifications for various applications.
How is the purity of gasoline enhanced through refining?
Reforming, isomerization, and alkylation transform low-octane hydrocarbons into high-octane components during the refining process, thereby improving the quality of gasoline. Hydrodesulfurization is also utilized to eliminate sulfur compounds, ensuring environmental compliance and reducing air pollution.
What byproducts result from the extraction of petroleum?
A: The petrol extraction procedure yields several valuable byproducts, including diesel, jet fuel, lubricants, and various petrochemicals utilized in the production of plastics, chemicals, and other products.
How is gasoline delivered to gas stations for consumers?
A: Once refined, gasoline is transported from refineries to distribution centers and gas stations via pipelines, ships, trucks, or railroads. The mode of transportation may vary based on the location and infrastructure.
Can gasoline be extracted from sources other than crude oil?
A: Although gasoline is predominantly extracted from crude oil, ongoing efforts are to investigate alternative sources of gasoline production, including biofuels derived from renewable resources such as plants and algae. Nevertheless, as of my most recent knowledge update in September 2021, crude oil continues to be the primary source of gasoline production.