What are the three aspects of information security?
This is the third and final article in a series discussing the three-pillar cyber security strategy. The first two pillars are called “people” and “process,” and the third and final pillar is called “data and information.”
Primarily, the original CIA defined the technical components of information security as confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and availability. These are all critical aspects of information security. For information to be deemed confidential, it must be impossible for unauthorized parties to produce it.
The maintenance of access control ensures that users are restricted to creating only the resources and services to which they are named and that users are allowed access to resources to which they have a reasonable expectation of having access.
A person who transmits a message cannot deny sending it, nor can a recipient deny receiving it. This is the meaning of the term “non-repudiation,” which is applicable in both directions. In addition to these technical components, the conceptual scope of data security is vast and encompasses numerous aspects.
The protection of data and information is the most technically involved and tangible of the three pillars. Our data sources include information technology (IT), operational technology (OT), personal data, and business data. It must be subjected to the appropriate management and safeguards at each stage.
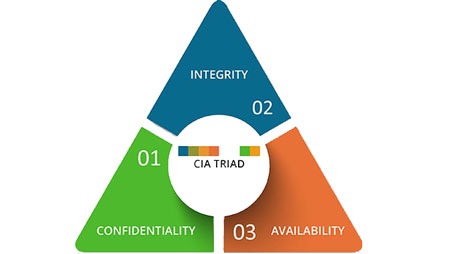
What is the CIA triad?
A crucial concept when discussing data and information is the CIA trinity. The CIA triangle is a method for safeguarding sensitive data consisting of these three elements: confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Each component represents a primary objective that must be achieved to guarantee information security.
The following section discusses the three pillars that comprise the CIA triad:
-
Confidentiality: This section is often associated with encryption and secrecy. In this discussion, data confidentiality refers to the restriction of information access to authorized parties. When a statement is said to be kept confidential, it has not been altered by a third party, and personal information is not disclosed to individuals who do not need it or should not have access to it. For the sake of confidentiality, information must be organized according to the level of sensitivity of the data and the individuals who need access to it. Multiple actions, such as hacking or social engineering, could result in a violation of confidentiality.
-
Integrity: The term “data integrity” refers to the assurance that the data has not been modified or degraded during transmission or after submission. It is the assurance that no unauthorized changes have been made to the data, whether they were created intentionally or unintentionally. The integrity of the data could be compromised during transmission at two distinct points: first, while the data are being submitted or transmitted, and second, when the document is being stored in the database or collection.
-
Availability: This indicates that the data is accessible to authorized users when required. For a system to demonstrate its availability, it must have fully operational computing systems, security controls, and communication channels. Critical systems, such as those used for power generation, medical equipment, and safety systems, are frequently subject to stringent availability requirements. These systems must resist cyberattacks and include safeguards against power outages, hardware malfunctions, and other events that impact availability.
Because collaborative spaces need to be consistent and well-maintained at all times, one of the most significant challenges is availability. Users of such systems need to be able to access the information they need with little delay. Redundant systems may be already set up to provide a high level of fail-over. The idea of a system’s practicability can also be included within the umbrella of the availability concept.
When information is kept or communicated, it is essential to maintain its integrity and confidentiality intact. This is what is meant by the term “information security.” A breach in information security occurs whenever information is accessed by individuals or parties that are not authorized to do so. Breach of security could have been caused by hackers, intelligence agencies, thieves, competitors, employees, or any number of other people or groups. Additionally, people who appreciate and seek to maintain their privacy are interested in information security since it protects their privacy.
The CIA triad is a model that breaks down the three most important aspects of data and information protection, each of which can serve as a point of reference when developing a security policy for a company. Establishing and maintaining the organization’s security policies may be challenging; nevertheless, utilizing the three-pillar strategic approach to cyber security will allow you to identify and manage cyber security threats in an organized and all-encompassing manner.
Conclusion
The CIA triad is a critical concept when discussing data and information. Confidentiality, integrity, and availability are the three primary tenets of the CIA triangle, a methodology for protecting sensitive data that consists of these three elements. Each component stands for a primary goal that must be accomplished to ensure information security.
Weirdnewsera says that you might not find any other platform that gives you all the content about health, sports, business, technology, and entertainment.
FAQs
What are the three main categories of IT security?
Technical, administrative, and physical controls are the three primary categories of IT security controls. It may be preventative, detective, corrective, compensatory, or deterrent to implement a security control.
What are the top three information security threats?
Malware attacks are the primary types of information security threats. Social manipulation assaults. Attacks on software supply chains.
What are the three principal goals of information security?
Typically, the primary objectives of InfoSec are to ensure the confidentiality, availability, and integrity of company information.
What are the four characteristics of information security?
Protection, Detection, Verification, and Reaction are the four components of a successful security system. These are the essential principles for adequate security on any site, be it a small independent business with a single location or a large multinational corporation with thousands of locations.